.
What is a Natural Gas Filter Separator?
1. First-Stage Regulators These are used in high-pressure natural gas systems to reduce pressure before it reaches the second stage. They are typically utilized in industrial settings.
People used to call it a pressure reducer, only to pay attention to its function of reducing voltage, and neglected its ability to stabilize voltage. The ingenious and fine design of the voltage regulator is precisely reflected in its voltage stabilizing ability. This article intends to make a detailed explanation in this respect. The following figure is the structural diagram of the pressure regulator, which is mainly composed of handwheels, intake pipe, upper valve cover, lower valve cover, rubber membrane, intake nozzle, valve pad, a small lever, air outlet and other components.
The Smart Regulator Revolutionizing Compliance and Efficiency in Business
PRVs also enhance the longevity of equipment. By maintaining stable pressure, these valves help reduce wear and tear on pumps, pipes, and other components, leading to lower maintenance costs and extending the overall lifespan of the system. Furthermore, consistent pressure can improve the performance of various processes, ensuring that systems operate smoothly and effectively.
Natural gas is increasingly being recognized as a crucial element in the global energy landscape. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges posed by climate change and the urgent need for cleaner energy sources, natural gas emerges as a pragmatic solution that bridges the gap between traditional fossil fuels and renewable energy.
How Pressure Reducing Regulators Work
However, as the LNG market grows, the challenges and environmental considerations associated with regasification equipment cannot be overlooked. The construction and operation of regasification facilities can have ecological impacts, such as water usage and emissions from auxiliary systems. Therefore, companies are increasingly investing in innovative technologies and practices to mitigate these environmental concerns, including the use of renewable energy sources in the vaporization process.
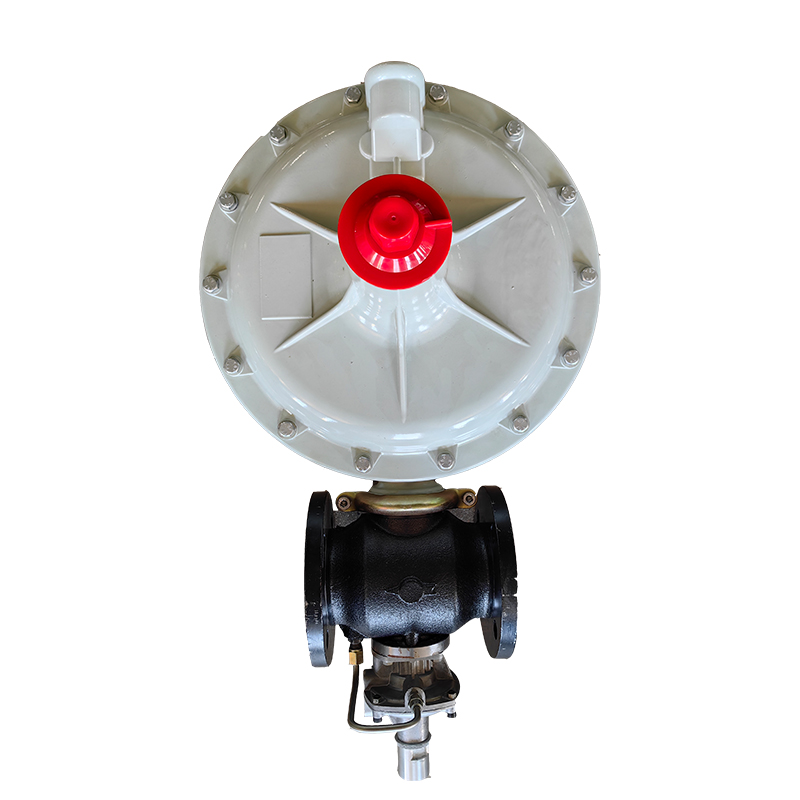 محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز الطبيعي. These components work together to control the flow and pressure of the gas, ensuring that it is maintained at a safe and consistent level. Pressure control valves automatically adjust the pressure of the gas based on the demand, while regulators maintain the pressure within a specific range.
محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز الطبيعي. These components work together to control the flow and pressure of the gas, ensuring that it is maintained at a safe and consistent level. Pressure control valves automatically adjust the pressure of the gas based on the demand, while regulators maintain the pressure within a specific range.Different types of reducers are available to handle various gases, including natural gas, propane, oxygen, and many others. Some models are designed for high-flow applications, while others are more suitable for low-flow systems. The choice of a specific gas pressure reducer depends on factors such as the type of gas, desired pressure range, flow rates, and application requirements.

Conclusion
Gas pressure regulator valves are indispensable components across a range of applications, providing safety and efficiency in gas management. Understanding their operation, types, and importance can help users make informed decisions regarding their installation and maintenance. With proper care, these regulators can ensure a reliable flow of gas, enhancing the safety and performance of various systems.
1. Single-Stage Regulators These are typically used for low-pressure applications. They reduce the pressure in a single step. Single-stage regulators are straightforward and are commonly found in residential settings.
The Rise of Superchargers Revolutionizing Electric Vehicle Charging
What are Air Control Valves?
Gas pressure reducers operate on the principle of pressure regulation. When gas enters the reducer, it is subjected to a diaphragm mechanism that responds to changes in downstream pressure. As the downstream pressure fluctuates, the diaphragm moves to either open or close the inlet of the gas flow, maintaining a constant output pressure.
- Air Conditioning and Refrigeration In HVAC systems, gas heat exchangers are essential for transferring heat from indoor air to the outside environment, contributing to efficient climate control.
3. Chemical Production The syngas obtained from gasification can serve as a feedstock for producing chemicals and materials such as ammonia, which is essential for fertilizers.
3. System Longevity Proper pressure management through the use of reducers can extend the lifespan of equipment. High-pressure gases can cause wear and tear on valves, pipes, and other components. By controlling pressure, reducers minimize stress on these parts, leading to decreased maintenance needs and increased reliability.
Gasification is an advanced thermal process that converts carbonaceous materials such as biomass, coal, and municipal solid waste into synthetic gas, also known as syngas. This syngas primarily consists of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and small amounts of carbon dioxide and methane. The concept of gasification has gained prominence due to its ability to provide a sustainable solution for waste management and energy production, making gasification equipment an essential component in the energy landscape.
In simple terms, a heat exchanger is a device designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids. These fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or may be in direct contact with each other. The primary goal is to either heat or cool a fluid without altering its phase, which makes heat exchangers indispensable in a myriad of processes.
In industrial contexts, precise pressure control is crucial for maintaining the operational integrity and safety of machinery and processes. Many industries rely on gas for manufacturing, from food production to chemical processing, making reliable gas pressure regulation a foundational aspect of their operations.
1. Electric Gate Valves These valves are primarily used for on/off control. They are designed for full flow, with minimal pressure drop when open, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
In political arenas, the influence of high-pressure advocacy organizations is evident in their ability to mobilize public opinion and drive policy changes. These organizations often employ strategies that leverage social media and grassroots campaigns to exert pressure on policymakers, demonstrating the power of collective action in high-pressure situations.
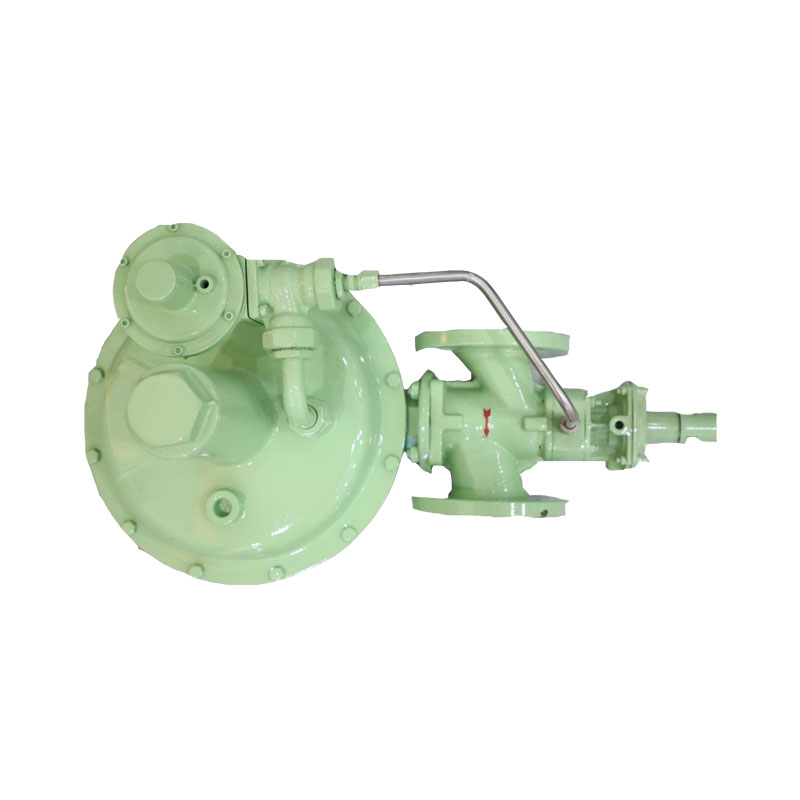
 These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations
These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations gas pressure regulator. They are often equipped with additional features such as pressure gauges, shut-off valves, and relief valves for added safety and functionality.
gas pressure regulator. They are often equipped with additional features such as pressure gauges, shut-off valves, and relief valves for added safety and functionality.In conclusion, Al-Madina Gateway Station stands as a testament to the harmonious blend of tradition and modernity. It is a gateway not only for travelers but also for the city of Medina as it navigates the complexities of the modern world while preserving its rich cultural identity. As it continues to evolve, the station will likely play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation in the region, ensuring that Medina remains a beacon of progress and hospitality for years to come.
Conclusion
Applications in Different Industries
In the contemporary dialogue surrounding energy resources and environmental sustainability, Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) has emerged as a significant player. As the world grapples with the pressing challenges of climate change and the depletion of traditional fossil fuels, CNG presents a viable alternative that combines economic efficiency with a reduced carbon footprint. This article explores what CNG is, its benefits, and the role it can play in a sustainable energy future.
In summary, the key difference between tapered roller bearings and ball bearings lies in their design and load-carrying capabilities. Tapered roller bearings are designed to support both radial and axial loads, while ball bearings are primarily intended for radial load support. Each type of bearing is tailored to meet specific operational requirements and environmental conditions in diverse industrial applications.
 Additionally, they are available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet specific performance requirements Additionally, they are available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet specific performance requirements
Additionally, they are available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet specific performance requirements Additionally, they are available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet specific performance requirements single deep groove ball bearing.
single deep groove ball bearing. This makes the bearing ideal for applications where high speeds and heavy loads are common This makes the bearing ideal for applications where high speeds and heavy loads are common
This makes the bearing ideal for applications where high speeds and heavy loads are common This makes the bearing ideal for applications where high speeds and heavy loads are common 51118 bearing.
51118 bearing.
 The conical surfaces are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for use in harsh environments such as those found in the oil and gas industry The conical surfaces are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for use in harsh environments such as those found in the oil and gas industry
The conical surfaces are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for use in harsh environments such as those found in the oil and gas industry The conical surfaces are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for use in harsh environments such as those found in the oil and gas industry tapered thrust bearing. The materials used to manufacture these bearings, such as chrome steel or ceramic, are also highly resistant to corrosion and wear, further extending their lifespan.
tapered thrust bearing. The materials used to manufacture these bearings, such as chrome steel or ceramic, are also highly resistant to corrosion and wear, further extending their lifespan.